Steady Concentration Peritoneal Dialysis (SCPD)
SCPD is a next-generation approach to peritonal dialysis (PD). With stable dialysate glucose levels, a gentle and consistent fluid removal is maintained during the entire PD dwell, improving treatment outcome
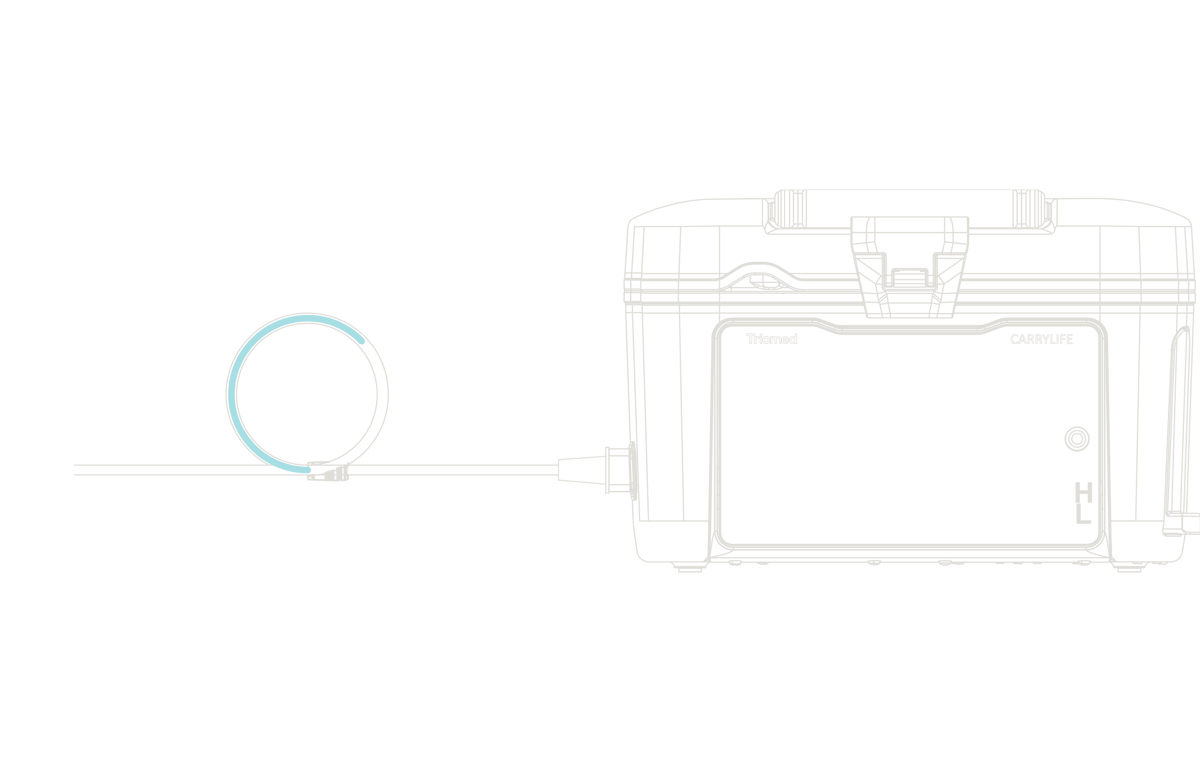

Rethinking PD with SCPD
-
Triomed has developed a new technology based on SCPD, Carry Life UF, to address the key limitations of conventional PD, to become the preferred dialysis option and enable patients to stay on PD longer.
-
By continuously adding glucose to the dialysate fluid, SCPD maintains the osmotic gradient across the patient’s peritoneal membrane, thereby offering a ultrafiltration advantage over standard PD.
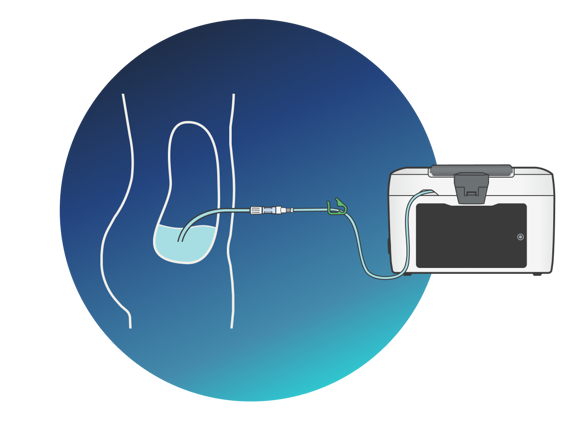
The Carry life UF Technology - Principle of Treatment
-
Glucose absorption from the dialysis fluid normally results in reduced ultrafiltration rate during the dwell. With Carry Life UF glucose is continuously added during treatment to compensate for this absorption.
-
The glucose solution is diluted within the device in a small portion of the dialysis fluid to avoid exposing the peritoneum to a high glucose concentration. The system is used with a low-strength glucose PD solution for the initial fill.

SCPD – Addressing Key Challenges in PD
Conventional PD often relies on high-glucose solutions, which may damage the peritoneal membrane and contribute to metabolic complications over time. Triomed’s Carry Life UF systems are designed to mitigate these risks while enhancing treatment outcomes and patient quality of life.
Key Benefits of Triomed SCPD
-
Improves glucose efficiency
-
Reduces reliance on hypertonic glucose solutions
-
Lower risk of metabolic complications
-
Decreases risk of peritoneal membrane burnout
-
Smaller cyclers and reduced fluid needs, improves patient independence and home storage feasibility
-
Tailored treatment delivery, increases flexibility and personalization of care

Optimized Fluid Management with Carry Life UF
-
Increased Fluid Removal
Fluid management is a major challenge with PD. The prevalence of fluid overload in PD patients is in the range of 56 to 73 % [1-3], with 25 % of patients experiencing severe fluid overload [4]. Inadequate fluid removal in PD patients leads to increased mortality, morbidity, and technique failure [5,6].
By maintaining the osmotic gradtient the Carry Life UF treatment had a four times higher fluid removal four times compared to a 2.27% glucose CAPD dwell [7]. The Carry Life UF treatment also removed fluid in patients who had a net absorption of fluid with a standard 2.27% glucose CAPD dwell. The UK Renal Association recommends that dialysis regimens resulting in fluid reabsorption should be avoided [8].
-
Increased Sodium Removal
Adequate sodium removal is a major challenge in PD, and low sodium removal contributes to fluid overload, hypertension and mortality disease in PD patients [6,9,10]. With the SCPD method, continuous ultrafiltration results in an increase in both convective and diffusive sodium removal. Carry Life UF treatment increased sodium removal four times compared to a 2.27 % glucose CAPD dwell [7].
-
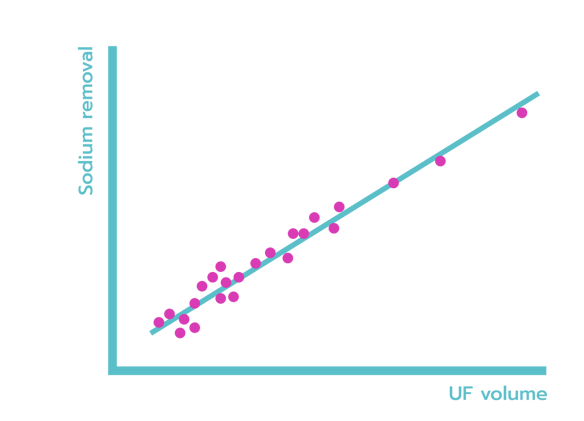
Predictable Sodium Removal
Total daily sodium removal should ideally reflect the daily sodium intake, which in average is 150-200 mmol/day.
In CAPD, the dialytic sodium removal correlates closely with the UF volume (approximately 125 mmol/L UF; r=0.94) [10], but for many CAPD patients the dialytic sodium removal is inadequate due to a low UF volume. In APD, short PD cycles and sodium retention result in removal of a hypotonic ultrafiltrate. Sodium removal with APD is about 50-100 mmol/L UF and cannot be predicted by the UF volume (r=-0.07) [10].
SCPD using the Carry Life UF system results in an ultrafiltration fluid with a sodium concentration similar to CAPD and with a sodium removal which correlates closely with the UF volume (121 mmol/L UF; r=0.98).
-
Reducing the Need for Hypertonic Glucose PD Solutions
The Carry Life UF is used with a low glucose strength PD solution, and the dialysate glucose concentration is stabilized at a level lower than the glucose concentration of hypertonic (≥2.27 % glucose) PD solutions [7]. Exposure of the peritoneal membrane to high glucose concentrations is therefore reduced when using the Carry Life UF system.

-
Increased Glucose Efficiency
Glucose based PD may lead to weight gain and associated adverse metabolic effects. A PD therapy that enables adequate fluid removal while limiting glucose uptake provides a benefit to PD patients. With SCPD glucose can be used more efficiently. Glucose UF efficiency was increased up to 2.9 times with the Carry Life UF system compared to a 2.27 % glucose CAPD dwell [7].